Pure CSS Bar Graphs with Graceful Mobile Fallbacks
2020-12-08
I recently published a new open source project, Flexbox Bar Graphs, and wanted to share a simple breakdown of how it was built. It isn’t anything mind-blowing, but I like the idea of placing bar graphs in a web page with zero Javascript.
So in the end, this is what our bar graphs will look like on desktop:
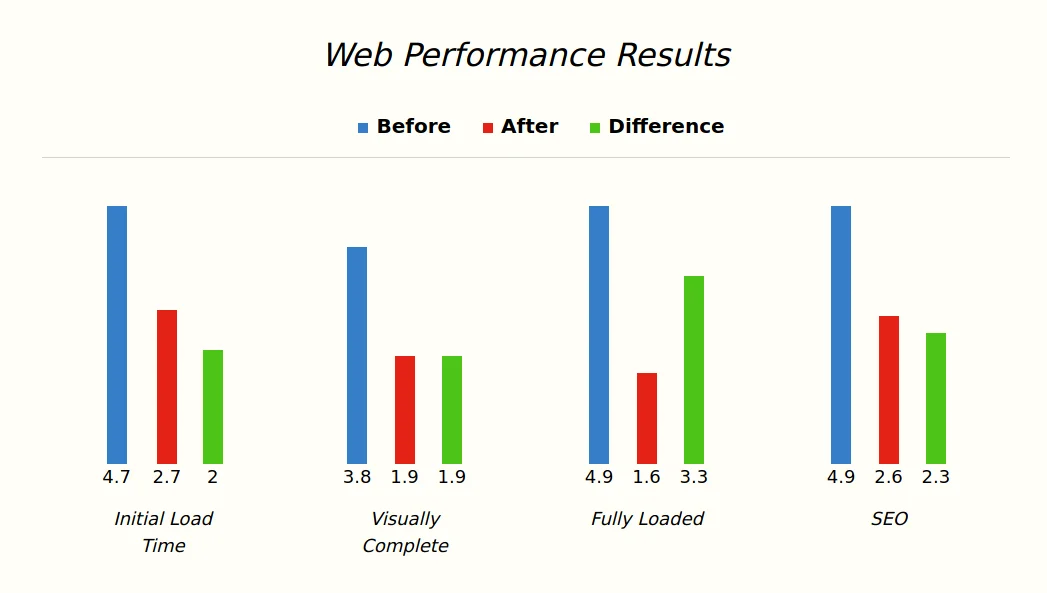
And this is how it will look on smaller devices:
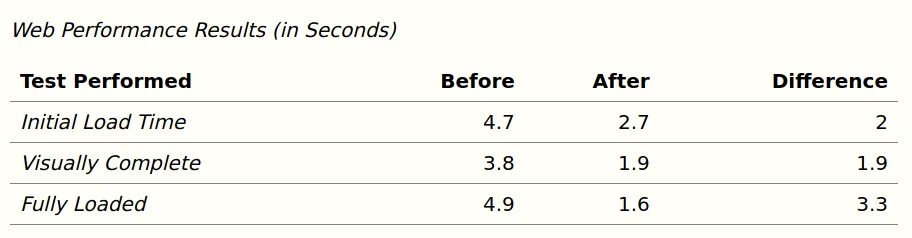
Let’s get into the details!
The HTML
The main “secret” of this project is that our graphs are constructed out of HTML tables. Now before you freak out - this is perfectly fine and works in our favor quite well.
- If the user has JS disabled –> they will still see our graphs
- If the user has CSS disabled –> they will see a standard data table set
All bases are covered!
<!-- Using a basic table with our custom data-id -->
<table data-id="flexbox-bar-graph">
<caption>Web Performance Results</caption>
<thead>
<tr>
<th>Test Performed</th>
<th>Before</th>
<th>After</th>
<th>Difference</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
<tr>
<th>Initial Load Time</th>
<td>
<!--
WTF are these CSS variables?
See the CSS section below
-->
<span style="--data-set:4.7/5;"></span>
<p>4.7</p>
</td>
<td>
<span style="--data-set:2.7/5;"></span>
<p>2.7</p>
</td>
<td>
<span style="--data-set:2/5;"></span>
<p>2</p>
</td>
</tr>
</tbody>
</table>
Nothing crazy is happening here - just your standard HTML table structure. The one main thing to notice is the --data-set CSS variable placed inline on each data point. This will be important for our CSS to configure the individual bar graphs properly.
The CSS
This might look overwhelming if I just dumped the whole CSS file in one big code block, so instead I’m going to break them down into two parts:
- Baseline styling (mobile)
- Desktop styling
Baseline
Here we target just our table elements with the data-id of flexbox-bar-graph. This allows us to avoid worrying about adding classes or IDs and also avoids conflicts with other non-graph styled tables in our projects.
The base :root element holds all of our bar graph colors. Change these as you see fit!
/* Bar Graph color variables */
:root {
--bar-color-1: #357EC7;
--bar-color-2: #E42217;
--bar-color-3: #4CC417;
--bar-color-4: #7D0541;
--bar-color-5: #FFD801;
}
[data-id="flexbox-bar-graph"] {
border-collapse: collapse;
margin: 4rem 0 6rem;
width: 100%;
}
[data-id="flexbox-bar-graph"] caption {
text-align: left;
}
[data-id="flexbox-bar-graph"] thead th {
text-align: right;
}
[data-id="flexbox-bar-graph"] thead th:nth-child(1),
[data-id="flexbox-bar-graph"] tbody th {
text-align: left;
}
[data-id="flexbox-bar-graph"] tbody th {
font-weight: normal;
font-style: italic;
}
[data-id="flexbox-bar-graph"] tbody td {
text-align: right;
}
[data-id="flexbox-bar-graph"] tbody td p {
margin: 0;
}
Desktop
Now we set your “visual” bar graphs to show at a set width (in this example it is 1000px and above). That way the “default” styling can target the mobile device screen sizes.
- The
thead tr th:nth-child(x):beforeelements create the square “legends” beside each individual data point heading - The
tbody tr td:nth-of-type(x) spanelements are the bars themselves
@media(min-width: 1000px) {
[data-id="flexbox-bar-graph"] {
background: transparent;
display: block;
min-height: 400px;
padding: 0;
position: relative;
width: 100%;
}
[data-id="flexbox-bar-graph"] caption {
display: block;
font-size: 2rem;
text-align: center;
width: 100%;
}
[data-id="flexbox-bar-graph"] thead {
display: block;
margin: 2rem 0 3rem;
width: 100%;
}
[data-id="flexbox-bar-graph"] thead tr {
border-bottom: 1px solid lightgrey;
display: flex;
justify-content: center;
padding-bottom: 1rem;
}
[data-id="flexbox-bar-graph"] thead tr th {
display: inline-block;
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
position: relative;
text-align: right;
}
[data-id="flexbox-bar-graph"] thead tr th:before {
content:'';
display: inline-block;
height: 10px;
margin: 0 0.5rem 0 2rem;
position: relative;
width: 10px;
}
[data-id="flexbox-bar-graph"] thead tr th:nth-child(1),
[data-id="flexbox-bar-graph"] thead tr th:nth-child(1):before {
display: none;
}
[data-id="flexbox-bar-graph"] thead tr th:nth-child(2):before {
background: var(--bar-color-1);
}
[data-id="flexbox-bar-graph"] thead tr th:nth-child(3):before {
background: var(--bar-color-2);
}
[data-id="flexbox-bar-graph"] thead tr th:nth-child(4):before {
background: var(--bar-color-3);
}
[data-id="flexbox-bar-graph"] thead tr th:nth-child(5):before {
background: var(--bar-color-4);
}
[data-id="flexbox-bar-graph"] thead tr th:nth-child(6):before {
background: var(--bar-color-5);
}
[data-id="flexbox-bar-graph"] tbody {
display: flex;
justify-content: space-between;
min-height: 300px;
width: 100%;
}
[data-id="flexbox-bar-graph"] tbody tr {
display: flex;
flex-direction: column-reverse;
flex-wrap: wrap;
justify-content: flex-end;
padding: 0 50px;
position: relative;
width: 100%;
}
[data-id="flexbox-bar-graph"] tbody tr th {
font-size: 90%;
position: absolute;
text-align: center;
top: 100%;
width: calc(100% - 100px);
}
[data-id="flexbox-bar-graph"] tbody tr td {
align-items: center;
display: flex;
flex-direction: column;
height: 95%;
justify-content: flex-end;
}
[data-id="flexbox-bar-graph"] tbody tr td span {
display: block;
height: calc(var(--data-set) * 100%);
width: 20px;
}
[data-id="flexbox-bar-graph"] tbody tr td:nth-of-type(1) span {
background: var(--bar-color-1);
}
[data-id="flexbox-bar-graph"] tbody tr td:nth-of-type(2) span {
background: var(--bar-color-2);
}
[data-id="flexbox-bar-graph"] tbody tr td:nth-of-type(3) span {
background: var(--bar-color-3);
}
[data-id="flexbox-bar-graph"] tbody tr td:nth-of-type(4) span {
background: var(--bar-color-4);
}
[data-id="flexbox-bar-graph"] tbody tr td:nth-of-type(5) span {
background: var(--bar-color-5);
}
[data-id="flexbox-bar-graph"] tbody tr td p {
font-size: 90%;
margin: 0;
text-align: center;
}
}
Bonus Styling
In the Flexbox Bar Graph repo, I’ve also included the ability to display these bar graphs horizontally, like so:
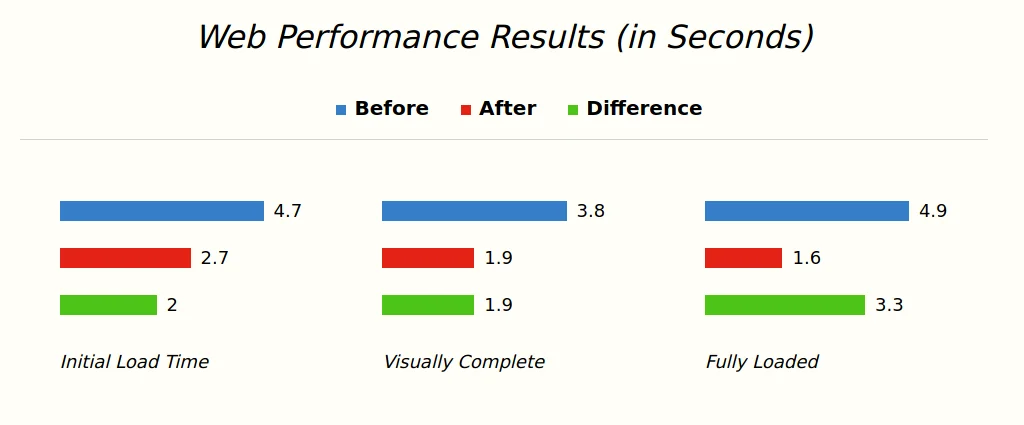
The change in CSS is actually quite simple to pull this off - you just need to include the data-layout attribute on the table itself.
[data-layout="horizontal"] tbody {
min-height: auto;
}
[data-layout="horizontal"] tbody tr {
flex-direction: column;
padding: 0 40px;
}
[data-layout="horizontal"] tbody tr th {
width: calc(100% - 80px);
}
[data-layout="horizontal"] tbody tr th {
text-align: left;
top: calc(100% + 20px);
}
[data-layout="horizontal"] tbody tr td {
flex-direction: row;
height: auto;
justify-content: start;
margin: 10px 0;
}
[data-layout="horizontal"] tbody tr td span {
height: 20px;
width: calc(var(--data-set) * 100%);
}
[data-layout="horizontal"] tbody tr td p {
margin-left: 10px;
}
That’s All Folks!
That just about sums things up. Feel free to check out the Github repo itself, open any issues you find or fork it for your own!